Narrative Review of Clinical Impact of Head-Hip Offset Following Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery
Article information
Abstract
In adult spinal deformity (ASD) surgery, mechanical failure (MF) has been a significant concern for spine surgeons as well as patients. Despite earnest endeavors to prevent MF, the absence of a definitive consensus persists, owing to the intricate interplay of multifarious factors associated with this complication. Previous approaches centered around global spinal alignment have yielded limited success in entirely forestalling MF. These methodologies, albeit valuable, exhibited limitations by neglecting to encompass global balance and compensatory mechanisms within their purview. In response to this concern, an in-depth comprehension of global balance and compensatory mechanisms emerges as imperative. In this discourse, the center of gravity and the gravity line are gaining attention in recent investigations pertaining to global balance. This narrative review aims to provide an overview of the global balance and a comprehensive understanding of related concepts and knowledge. Moreover, it delves into the clinical ramifications of the contemporary optimal correction paradigm to furnish an encompassing understanding of global balance and the current optimal correction strategies within the context of ASD surgery. By doing so, it endeavors to furnish spine surgeons with a guiding compass, enriching their decision-making process as they navigate the intricate terrain of ASD surgical interventions.
INTRODUCTION
Contemporary research endeavors in the field of spine surgery have underscored the multifaceted nature of mechanical failure (MF) subsequent to adult spinal deformity (ASD) surgery. The reported incidence of MF, including proximal junctional failure/kyphosis, distal junctional failure/kyphosis, and implant loosening, has exhibited a wide-ranging prevalence, spanning from 17% to 61.7% across various studies [9,10,15,19,24,29,31,40,42]. Numerous methodological approaches have been developed to achieve optimal correction and preclude MF in the context of ASD treatment. The Scoliosis Research Society (SRS)-Schwab classification and Global Alignment and Proportion (GAP) score represent prominent examples of such strategies, centering on the meticulous consideration of spinal alignment [37,44]. However, it is important to acknowledge that ongoing debates persist, and a definitive consensus concerning the most favorable parameters remains elusive [2,33]. This complexity signifies that while the pursuit of appropriate spinal alignment, encompassing well-aligned global spinal alignment (GSA), is a pivotal facet, its sole consideration might fall short in effectively preventing MF in the context of ASD surgery. Consequently, a more comprehensive spectrum of factors necessitates consideration [15-18,22,23,26].
Of particular significance in this landscape is the pivotal role of global balance, which has garnered extensive attention from researchers [1,32]. The centrality of the center of gravity (COG) and the imperative for a holistic evaluation of the entire body have been repeatedly underscored in the literature [11,23,26,34,36,39]. Technological advancements, epitomized by innovations like the EOS whole-body imaging system (EOS Imaging, Paris, France), have empowered the comprehensive analysis of the entire body while minimizing radiation exposure and distortion [5,8]. This advancement has dramatically motivated research on global balance and compensatory mechanisms [8,11,12,23].
This narrative review seeks to provide a comprehensive and insightful exploration of the clinical implications surrounding global balance and COG, with a specific focus on devising an optimal correction strategy for addressing complications arising from ASD surgery. This undertaking aims to facilitate a deeper comprehension among readers regarding pertinent concepts and insights, including the intricate interplay of compensatory mechanisms.
GLOBAL BALANCE AND COMPENSATORY MECHANISM
Concept of global balance
Balance within our body signifies a state where muscular forces are harmoniously counteracted, resulting in the minimized and efficient interplay between agonist and antagonist muscle groups [23]. Dubousset [6] succinctly encapsulated this notion of balance in 1994, terming it the ‘cone of economy,’ which pertains to the global balance encompassing the entire body. The human skeletal system operates similarly with a “reversed pendulum” while standing. This process initiates from the support polygon formed by both feet and progresses along the lower limb skeleton, involving the ankles, knees, hip joints, and pelvis. It then continues through the spinal segments, culminating in the cephalic vertebra. The latter functions as a pendulum to achieve horizontal vision and equilibrium. These components play a crucial role in sustaining the distinctive upright posture observed in humans, where the “cone of economy” remains harmoniously balanced with minimal muscular effort.
To evaluate global balance, overall assessment of the whole body is mandatory, and various studies have been conducted on radiographic methods [8,27,28,30]. One monumental leap in the field has been the introduction of the EOS imaging system. The development of EOS imaging system has revolutionized how we perceive and analyze global balance [8,23,30]. The EOS imaging system was invented to overcome the limitations of conventional radiography [25]. The 3-dimensional technique facilitates the examination of bilateral long-length images from foot to cranium in either the standing or seated position. The advantage of EOS imaging system is that it enhances image quality and minimizes image distortion with a relatively low radiation dose [8,30].
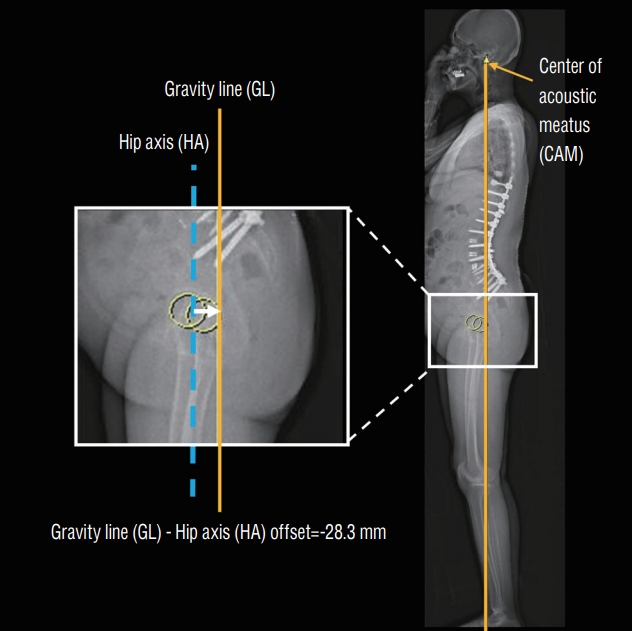
Such radiographic advancements have been pivotal for researchers in delineating optimal global balance more accurately and enabling its clinical application. Multiple research exhibits that the COG emerged as a key factor in comprehending global balance [1,11-13,21,32,34,36,39]. The COG was assessed using force platforms (a device measuring the vertical projection of the sum of ground reaction forces on a standing person). This resultant vertical trajectory is termed the gravity line (GL), representing the COG in individuals [34]. In a optimal-balanced population, GL is usually located posterior to the femoral heads [34,36]. Historically, the C7 plumb line (C7PL) has been wielded as a surrogate for COG due to its accessible and pragmatic utility in measuring sagittal trunk balance [20,43]. Nonetheless, contemporary research has unveiled its discordance with the GL defined as occiput-trunk discordance, highlighting a pressing need for more reflective metrics of COG [43].
An emerging surrogate anatomical landmark, center of acoustic meatus (CAM), has attracted significant attention since the elucidative research by Hasegawa et al. [11,12]. Utilizing the EOS imaging system in conjunction with force platforms, they embarked on an analytical exploration of COG, discovering a congruence between the COG and CAM or GL, remarkably unaffected by the progression of age. This implies that the CAM line (the vertical line starting from the center of bilateral CAM) can be considered identical to the GL (Fig. 1). Further investigation revealed an age-mediated shift in the relationship between GL and bony landmarks, wherein the GL tends to approximate the hip axis (HA; center of the bilateral femoral head) as people age more than sixties. Notably, the mean position of the HA consistently maintained an anterior position relative to the GL among asymptomatic cohorts [11,12].
Compensatory mechanism and global balance
Understanding the intricate interplay between compensatory mechanisms and global balance is a pivotal precursor to comprehending the clinical impact of global balance [16,23,25,26]. As aging and certain pathological conditions manifest, deterioration of the GSA may lead to imbalance [16,23,26]. In such scenarios, compensatory mechanisms become pivotal in upholding global balance, ensuring erect posture and facilitating a horizontal gaze [23,26,36]. Aging precipitates truncal stooping, which influences GSA. This is, however counteracted by compensatory mechanisms that encompass increased cervical lordosis, pelvic tilt (PT), and knee flexion [11]. Also, in patients with spinal pathologies, compensatory mechanisms occur step-by-step to maintain global balance by affecting GSA and other body factors from the thoracolumbar to the cervical spine and lower extremities [7]. When spinal deformity develops at any level, initial compensatory mechanisms typically initiate adjacent to the deformity. With the depletion of compensatory potential adjacent to the deformity, neighboring segments are sequentially enlisted to maintain balance and erect posture [3]. Roussouly and Pinheiro-Franco [35] proposed the following sequential mechanism of compensation for progressive kyphosis : 1) normal stage (slight pelvic retroversion and the C7PL aligned over the sacral endplate); 2) compensated stage (gradual loss of lumbar lordosis [LL] and further pelvic retroversion to keep the C7PL posterior to the femoral heads); and 3) decompensated stage (hip extension limits pelvic retroversion, which is compensated by knee flexion, and the C7PL passes forward to the femoral heads). The final posture, wellknown in severe kyphosis, involves maximum hip extension and flexed knees, resulting in extreme discomfort and inefficiency. It describes that patients with thoracolumbar malalignment exhibit compensatory changes in the form of cervical hyperlordosis, posterior pelvic shift, ankle dorsiflexion, knee flexion, hip extension, and pelvic retroversion [3,26].
Therefore, in specific situations with a risk of global balance disruption, compensatory mechanisms operate to maintain global balance affecting GSA and other body segments. Our body is persistently engaged in such compensatory mechanisms to sustain global balance, often allowing GSA to deviate from an ideal alignment while the global balance is preserved [1,23,25,26,32].
STRATEGIES FOR ASD SURGERY
There are two most widely used systems in ASD surgery. The SRS-Schwab classification utilizes three sagittal modifiers (optimal target : pelvic incidence [PI] minus LL <10°, sagittal vertical axis [SVA] <4 cm, PT <20°) to quantify deformity status and determine correction target. The Schwab sagittal modifier thresholds were based on the established correlations between radiographic parameters and health-related quality-of-life measures [37]. However, it has been observed that despite achieving optimal Schwab values postoperatively, mechanical complications persist [38,44]. It is believed that this stems from the incapacity of linear numerical parameters to cover the full spectrum of PI [44].
To address the limitations of linear numerical parameters like the SRS-Schwab classification, the GAP score was introduced by Yilgor et al. [44]. This innovative approach aimed to provide a more comprehensive analysis of the sagittal plane dynamics in patients undergoing ASD surgery. The GAP score serves as a valuable prognostic tool for anticipating potential mechanical complications in these patients. By incorporating this scoring system, surgeons gain enhanced insight into the patient’s condition, aiding in informed decisions regarding surgical approaches to achieve optimal outcomes while averting spinal deformity-related mechanical complications. The GAP score system is formulated as a metric that takes into account four sagittal factors : relative pelvic version, relative LL, lordosis distribution index, and relative spinopelvic alignment, each assessing the extent of deviation from the ideal spinal curvature. The GAP score considers the proportionate relationship between the optimal sagittal alignment and PI, with a higher GAP score indicative of a higher possibility of MF [44]. It is worth noting, however, that recent studies have yielded inconclusive findings, failing to establish a robust correlation between GAP scores and the incidence of MF [2,4,41].
In light of the insights above, the existing strategies employed for correcting ASD exhibit certain limitations. These strategies conventionally concentrate on GSA and fixed spinal segments, often neglecting the intricate dynamics of global balance and compensatory mechanisms [2,4,13,15,16,33]. These findings underscore the inherent limitations of strategies that predominantly emphasize isolated segments of the spine. The burgeoning need for a more comprehensive comprehension of global balance, encompassing both fused and unfused spinal segments and acknowledging the dynamic compensatory potential of the entire body, has come to the forefront of research and clinical discourse [1,14,16,33]. The evolving concepts necessitate a paradigm shift towards a more holistic understanding, encompassing the static parameters and the intricate interplay of compensatory mechanisms and global balance for improved surgical outcomes after ASD surgery.
HEAD-HIP OFFSET
Because of the limitations mentioned earlier, there has been a suggestion to implement a concept of global balance and these approaches have been developed based on the insight that GL of the normal populations is situated near HA [1,11,23,32]. An et al. [1] initially reported that GL-HA offset significantly correlates with MF, in a study involving 65 patients who underwent surgical procedures for ASD between 2013 and 2019. These patients were followed up for a minimum of 2 years. The GL-HA offset was defined as the distance between the CAM line and the center of bilateral femur head (Fig. 2). Through logistic regression analysis, the results demonstrated that GL-HA offsets of -49.3 mm or more showed a significant increase in MF. Subgroup analysis dividing the cohort based on postoperative GL-HA values based on a -50 mm threshold revealed an odds ratio of 11.0 for the occurrence of MF in the group with GL-HA values of -50 mm or above (Figs. 3 and 4). However, the study did not explain the clinical impact when the GL-HA offset was positive (above 0 mm), indicating an under-correction state.
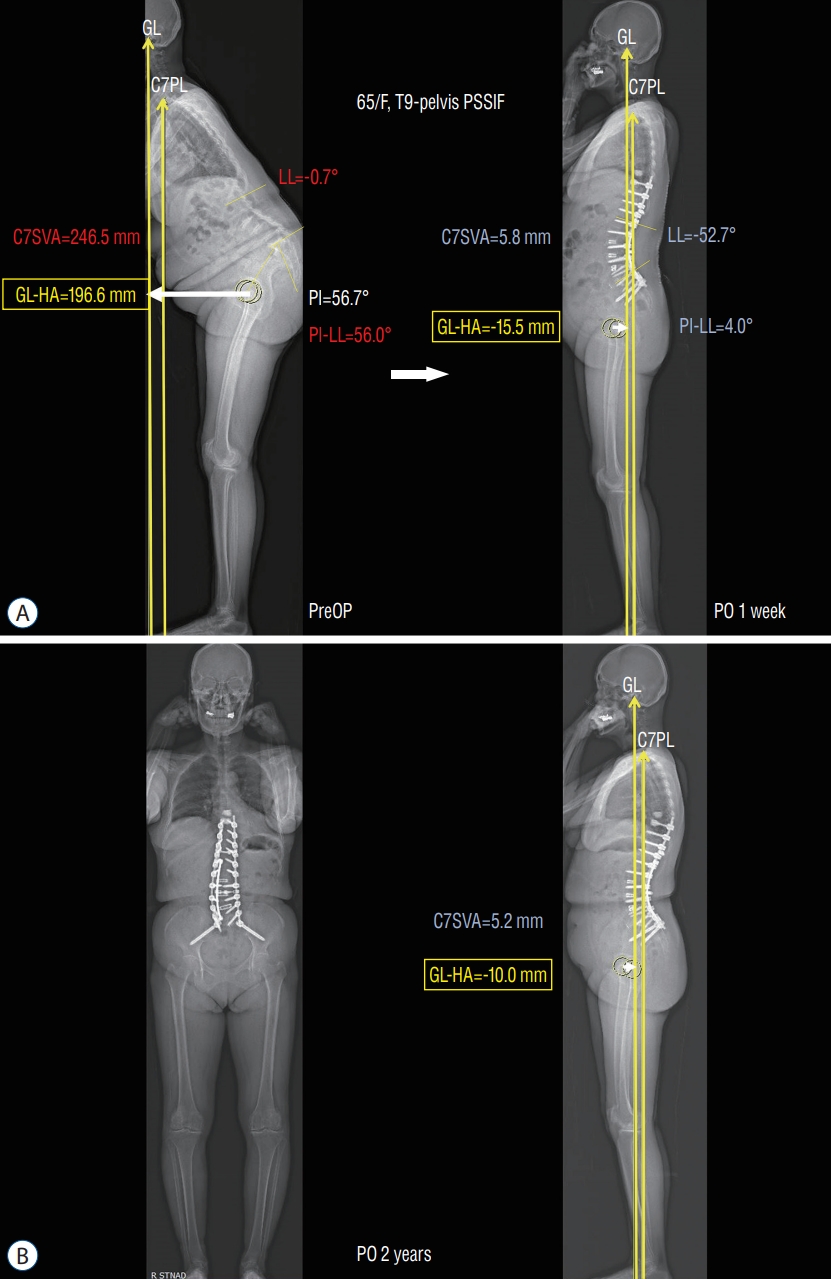
Immediate postoperative appropriate GL-HA offset having no mechanical failure. A 65-year-old female (F), PSSIF T9 to pelvis with multilevel posterior column osteotomy, including TLIF at levels L2/3, L3/4, L4/5, and L5/S1. A : The preoperative GL-HA offset of 196.6 mm was appropriately corrected to -15.5 mm postoperatively. It did not exceed the risk factor of -50 mm, which is associated with mechanical failure. B : The GL-HA value has been well maintained at -10.0 mm for 2 years postoperatively, and there have been no significant mechanical or clinical changes up to the present. PSSIF : posterior spinal segmental instrumentation and fusion, SVA : sagittal vertical axis, LL : lumbar lordosis, GL : gravity line, HA : hip axis, PI : pelvic incidence, preOP : preoperative, PO : postoperative.

Immediate postoperative inappropriate GL-HA offset with mechanical failure. A 70-year-old female (F), PSSIF T10 to pelvis and uninstrumented posterior fusion T9-10, prophylactic vertebroplasty (VP) T9, T10, therapeutic VP at L2 including decompressive laminectomy L1/2/3, bilateral foraminotomy at L5-S1. A : The preoperative GL-HA offset of 5.5 mm was excessively corrected to -128.9 mm postoperatively. It did exceed the risk factor of -50 mm, which is associated with mechanical failure. B : The GL-HA value has been changed at 11.0 mm for 3 years postoperatively, and it have resulted in bilateral rod fracture (red arrows) and symptoms of back pain. GL : gravity line, PSSIF : posterior spinal segmental instrumentation and fusion, PL : plumb line, LL : lumbar lordosis, PI : pelvic incidence, SVA : sagittal vertical axis, HA : hip axis, preOP : preoperative, PO : postoperative.
A similar approach has recently been applied. Mohanty et al. [32] introduced the cranial SVA to the centers of the hip (CrSVA-H), a measurement nearly identical to GL-HA, which aids in understanding undercorrected GL-HA. The CrSVA-H was defined as the distance between the vertical line of the cranial center of mass (CCOM) and the midpoint of the line drawn through the center of the two femoral heads (Fig. 5). CCOM means the nasion-inion line’s midpoint (the nose’s root to the external occipital protuberance), above and slightly in front of the acoustic meatus. The study was performed with a propensity score-matching, and patients were divided into two groups : CrSVA-H <20 mm (aligned cohort) vs. CrSVA-H >20 mm (malaligned cohort), respectively 27 individuals. The results showed, at the 2-year postoperative follow-up, the CrSVA >20 mm group (malaligned cohort) reported worse outcomes in SRS-22r function (p=0.0275), pain (p=0.0012), and mean total score (p=0.0109). Moreover, the group had a higher 2-year reoperation rate (22% vs. 7%; p=0.0412) compared with patients in the aligned cohort (CrSVA-H <20 mm).

Cranial sagittal vertical axis to the centers of the hip [18]. CrSVA-H (blue line) : the distance between the vertical line (yellow line) of the CCOM and the center of the two femoral heads. Nasion-inion line (yellow dashed line) : root of the nose to the external occipital protuberance, CCOM (midpoint of the nasion-inion line) : above and slightly in front of the acoustic meatus. CrSVA-H : cranial sagittal vertical axis to the centers of the hip, CCOM : cranial center of mass.
These studies highlight the significance of incorporating global balance measurements, such as GL-HA and CrSVA-H, in assessing the risk of MF and patient outcomes following ASD surgery [1,32]. However, there may be several limitations in practically applying such head-hip offset with current technology. For instance, when applying head-hip offset during surgery, various imaging methods, including intraoperative prone whole-spine lateral radiograph, can be considered. Practically, we have been utilizing digitalized radiographic machine which can fuse several radiographs to see from CAM to hip joints. However, it’s important to note that the actual head-hip offset concept is designed for the standing position and, with our current knowledge, we have not found an ideal imaging method that can truly reflect the head-hip offset in a standing position during surgery. Therefore, we need to make efforts to address this limitation and apply it more practically.
Nevertheless, a better understanding of these measurements can aid in making informed decisions regarding surgical correction, leading to improved treatment outcomes and patient satisfaction. Therefore, while further research appears to be necessary, considering the previous studies, correcting the GL to fall within the range of -5 cm (negative balance) to +2 cm (positive balance) from the HA seems appropriate to prevent MF in ASD surgery.
CONCLUSION
MF in ASD surgery remains an intricate challenge due to its multifactorial nature. Despite the myriad of strategies developed to curb its incidence, MF remains a formidable concern in spine surgery. The spotlight has been cast on the role of global balance as a pivotal determinant in averting MF. Assessing the body’s overall equilibrium demands a comprehensive evaluation, and the evolution in radiographic techniques has significantly bolstered our capabilities to examine global balance with precision, stimulating a plethora of research endeavors in this domain. In scenarios predisposed to imbalances, such as age-related changes or specific pathological conditions, compensatory mechanisms play an indispensable role in preserving global balance. Grasping the nuances of these mechanisms is cardinal for a profound understanding of the clinical implications of global balance. One of the emerging understandings is the predilection for the GL to converge near the HA, which has given rise to strategies like the head-hip offset. With insights into global balance and its intertwined compensatory mechanisms, the head-hip offset strategy equips spine surgeons with a refined perspective, facilitating informed decisions for establishing optimal correction benchmarks in ASD surgery.
Notes
Conflicts of interest
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Informed consent
This type of study does not require informed consent.
Author contributions
Conceptualization : SJH; Data curation : SK; Formal analysis : SK; Funding acquisition : SJH; Methodology : SK, SJH, JKL, KJK; Project administration : SJH; Visualization : SK, SJH; Writing - original draft : SK; Writing - review & editing : SJH, JKL, KJK
Data sharing
None
Preprint
None